WHAT IS?
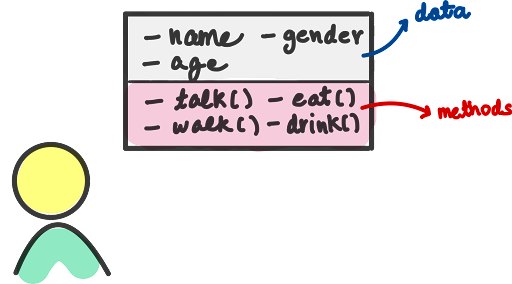
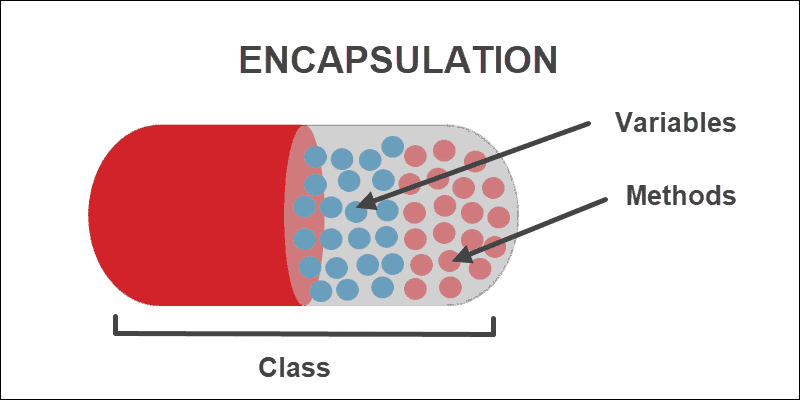
Encapsulation is one of the fundamentals of OOP (object-oriented programming). It refers to the bundling of data with the methods that operate on that data. Encapsulation is used to hide the values or state of a structured data object inside a class, preventing unauthorized parties’ direct access to them. Publicly accessible methods are generally provided in the class (so-called getters and setters) to access the values, and other client classes call these methods to retrieve and modify the values within the object.
The most important principle of object orientation is encapsulation: the idea that data inside the object should only be accessed through a public interface – that is, the object’s methods.
If we want to use the data stored in an object to perform an action or calculate a derived value, we define a method associated with the object which does this. Then whenever we want to perform this action we call the method on the object. We consider it bad practice to retrieve the information from inside the object and write separate code to perform the action outside of the object.
Encapsulation is a good idea for several reasons:
- The functionality is defined in one place and not in multiple places.
- It is defined in a logical place – the place where the data is kept.
- Data inside our object is not modified unexpectedly by external code in a completely different part of our program.
- When we use a method, we only need to know what result the method will produce – we don’t need to know details about the object’s internals in order to use it. We could switch to using another object which is completely different on the inside, and not have to change any code because both objects have the same interface.
We can say that the object “knows how” to do things with its own data, and it’s a bad idea for us to access its internals and do things with the data ourselves. If an object doesn’t have an interface method which does what we want to do, we should add a new method or update an existing one.
Some languages have features which allow us to enforce encapsulation strictly. In Java or C++, we can define access permissions on object attributes, and make it illegal for them to be accessed from outside the object’s methods. In Java it is also considered good practice to write setters and getters for all attributes, even if the getter simply retrieves the attribute and the setter just assigns it the value of the parameter which you pass in.
In Python, encapsulation is not enforced by the language, but there is a convention that we can use to indicate that a property is intended to be private and is not part of the object’s public interface: we begin its name with an underscore. Python also supports the use of a property decorator to replace a simple attribute with a method without changing the object’s interface.
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario